Types of Hair Loss: Alopecia Areata
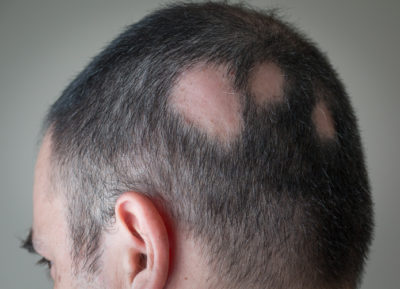
This type of hair loss can occur at any age but it is most common in people younger than 20, affecting men and women equally. If you’re reading this article, chances are you already have a few worries about your hair, or know someone who does.
If you are feeling down, defeated, alone or worried, we’re here to assure you that this battle does not need to be fought alone and you DO have options!
What Are The Symptoms Of Alopecia Areata?
Did you know there are seven different types of Alopecia? It’s important to diagnose exactly which type you may be dealing with before taking any steps towards regrowth. The majority of individuals diagnosed with Alopecia will begin to see hair regrowth within a year. That’s right; in all but about 10% of the cases, this is not a permanent condition (source). Due to the fact that in most cases the hair will grow back, you may decide not to treat your condition at all. However, we do suggest speaking with a member of our team to be sure that this is the cause of your recent hair loss and look into any options that may be available.
In very few cases, total loss of scalp and body hair can occur. The hair loss may come and go. Hair may fall out in one area and grow back in another. With patchy hair loss, the hair typically grows back in several months. While the regrowth is usually the same color and texture, it could grow back fine and white.
About 10% of people with this condition may never regrow hair. You are more likely to have permanent hair loss if you:
- Have a family history of the condition.
- Have the condition at a young age or for longer than one year.
- Have another autoimmune disease.
- Are prone to allergies (atopy).
- Have extensive hair loss.
- Have abnormal color, shape, texture, or thickness of the fingernails or toenails.
What Causes This Hair Loss?
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease. Autoimmune means that the body’s immune system attacks the body. When alopecia areata develops, the body attacks its own hair follicles. A person’s genetic makeup, combined with other factors, triggers this form of hair loss.
It is not known why alopecia areata or other autoimmune diseases occur. It is thought that something triggers the immune system to react against one or more of the body’s own tissues. Possible triggers include viruses, infection, medicines or other environmental factors. There is also an inherited factor, which makes some people more prone to autoimmune diseases (Source).
Are There Side Effects To Alopecia Areata?
Mild cases of alopecia areata regularly get better without treatment within a few months to a year. However, some cases include patchy baldness that may come and go over several months to a year. In this time, the size of the patches and the amount of hair loss varies. With more severe cases of hair loss; it is less likely the hair will grow back on its own. According to Patient Info, even if your hair grows back fully after an episode of alopecia areata, it is common to have one or more recurrences of the condition throughout your life. A few people who develop alopecia areata will progress to total scalp baldness (alopecia totalis). Even fewer people will lose all scalp and body hair (alopecia universalis).
If you are experiencing hair loss due to alopecia areata, it’s beneficial to talk to a hair restoration specialist. Your consultation will be held in a comfortable, private setting so you can openly discuss your hair loss concerns and determine which hair loss solution is right for you. There is no obligation to make a purchasing decision during the consultation.
How Can Alopecia Be Diagnosed?
Alopecia is diagnosed through a medical history as well as physical examination. Your doctor will ask you some simple questions regarding your hair loss, evaluate the patterns you may be having and examine your scalp. If the reason for your hair loss is not quickly determined, you should move forward with a small test to check for any diseases that could be causing this loss. These tests include:
- Hair Analysis. A doctor will take a sample of your hair and examine it under a microscope. A scalp sample is also sometimes taken.
- Blood tests, including testing for a specific condition, such as an overactive or under active thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism).
What Are Some Hair Loss Treatment Options?
Alopecia areata, as said before, is typically temporary. This type of hair loss doesn’t always require treatment, nor does it sometimes respond to treatment, but there are options available in cases where it is medically indicated. The following are some alopecia treatment options that have been show to work for both men and women, regardless of hair type:
- Wigs can be a common solution for people struggling with alopecia areata as they provide a temporary solution until the hair grows back or is restored.
- Low-Level Laser Hair Therapy is one of the most effective methods of treating early-stage androgenetic alopecia (genetic pattern hair loss) in both men and women.
- Enhanced Plasma Therapy (EPT) hair loss treatment therapy is a proactive treatment option for male and female patients experiencing thinning hair or hair loss. It’s an exciting non-surgical therapeutic option for hair loss sufferers who require stimulation of hair growth. EPT therapy has shown great promise in the treatment of androgenic alopecia.
Grow Your Hair Back™ Medical Hair Restoration | McLean, Virginia
At Grow Your Hair Back™ Medical Hair Restoration in McLean, Virginia, we are very proud to provide each of our clients with the latest advances in technology for clinically proven hair loss prevention and hair restoration solutions. Grow Your Hair Back™ Medical Hair Restoration is a recognized leader in multi-therapeutic hair loss treatments, hair transplants and hair restoration for men and women suffering from Alopecia, balding and thinning hair.